Get ready to uncover the secrets of the RFC 822 Mail Message Format in this informative article.
Introduction to RFC 822 Mail Message Format
RFC 822 is a standard format for email messages that was published in 1982. It defines the structure of email messages and provides guidelines for how they should be formatted and transmitted.
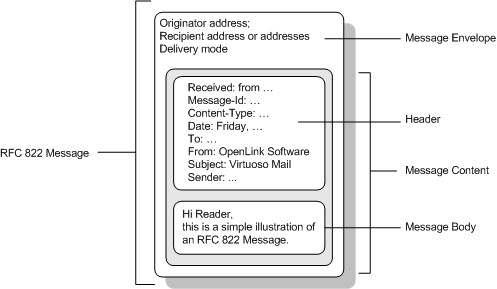
The format includes headers, which contain information about the sender, recipient, and subject of the message, as well as the date and time it was sent. It also includes the body of the message, which can include text, images, and other types of content.
Understanding the RFC 822 format is important for anyone who works with email, whether you’re a developer building email applications or a user trying to troubleshoot email issues. In this article, we’ll dive into the details of the RFC 822 format and explain how it works.
Components of RFC 822 Mail Message Format
- Header: Contains metadata about the message, including the sender, recipient(s), subject, and date.
- Body: Contains the actual content of the message, such as text, images, or other attachments.
- Fields: Components within the header that provide specific information about the message, such as the message ID or the content type.
- Addresses: The email addresses of the sender and recipient(s), which are listed in the header.
- Encoding: Specifies how the content of the message is formatted and transmitted, such as plain text or HTML.
- Structure: The organization of the message and its components, which must follow a specific format to be compatible with RFC 822.
Common Errors in RFC 822 Mail Message Format
The RFC 822 mail message format is widely used for email communication. However, there are some common errors that can occur when using this format. The most common errors include invalid email addresses, incorrect date and time formatting, and missing header fields. Another frequent error is the improper use of line breaks and whitespace, which can cause problems with message interpretation. It’s important to follow the RFC 822 standard closely to avoid these errors and ensure that your email messages are properly formatted and received by the intended recipients. By paying attention to these common errors, you can improve the effectiveness of your email communications and avoid potential misunderstandings.
Causes of Errors in RFC 822 Mail Message Format
The RFC 822 Mail Message Format is a widely used standard for email communication. However, errors can occur when sending or receiving emails due to various reasons. One common cause of errors is improper formatting of the email address, such as missing or extra characters, or using the wrong syntax. Another cause of errors is the use of non-standard characters or symbols in the email message, which may not be recognized by the recipient’s email client. Additionally, errors can occur when attachments are not properly encoded or when the email message exceeds the maximum allowed size. It is important to ensure that emails are properly formatted and adhere to the RFC 822 standard to avoid errors and ensure successful delivery.
Methods to Fix Errors in RFC 822 Mail Message Format
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Use a Validator | Use a validator tool to check the syntax of the RFC 822 mail message format. This tool can identify errors and suggest corrections. |
| Check Headers | Check the headers of the RFC 822 mail message format for errors. Ensure that the headers are properly formatted and contain all the required fields. |
| Check Body | Check the body of the RFC 822 mail message format for errors. Ensure that the body is properly formatted and contains all the required information. |
| Encode Non-ASCII Characters | If the RFC 822 mail message format contains non-ASCII characters, ensure that they are properly encoded using a character encoding scheme such as UTF-8. |
| Use a MIME Type | If the RFC 822 mail message format contains multimedia content, use a MIME type to properly format and transmit the content. |
| Use a Library | Use a library or framework that supports the RFC 822 mail message format to ensure that the format is properly handled and transmitted. |
Best Practices for Using RFC 822 Mail Message Format
- Use standard headers: RFC 822 defines a set of standard headers that should be used in mail messages. These include From, To, Subject, Date, and Message-ID. Using these headers ensures that your messages are compatible with most email clients and servers.
- Format headers correctly: Each header should be formatted in a specific way, with the header name followed by a colon and a space, and the header value on the following line. Make sure to follow this format for each header in your message.
- Include a message body: Every mail message should include a message body, which is the actual content of the message. The body should be separated from the headers by a blank line, and can be formatted using plain text or HTML.
- Encode special characters: If your message includes any special characters, such as non-ASCII characters or certain symbols, you will need to encode them using a specific encoding scheme. The most common encoding scheme is called MIME, and it allows you to include special characters in your message without causing any issues.
- Avoid spammy content: When creating a mail message, make sure to avoid using spammy content that could trigger spam filters. This includes using all caps in your subject line, including too many links or images in your message, and using certain trigger words like “guaranteed” or “free.”
- Test your messages: Before sending any mail messages using RFC 822 format, make sure to test them thoroughly to ensure they are compatible with different email clients and servers. This can help you avoid any issues or errors that could prevent your message from being delivered.

