Are you struggling with Wi-Fi or Ethernet connectivity issues due to a “Valid IP Configuration” problem? This article will provide you with simple and effective solutions to fix this issue and get your internet connection back up and running.
Understanding the “No Valid IP Configuration” Error
The “No Valid IP Configuration” error can occur when your Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection is unable to obtain a valid IP address. This can prevent you from accessing the internet or connecting to other devices on your network.
To fix this error, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can try:
1. Restart your router and modem. Sometimes, a simple reboot can resolve connectivity issues. Turn off your router and modem, wait for a few seconds, then turn them back on.
2. Update your network adapter drivers. Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause IP configuration problems. Visit the manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest drivers for your network adapter.
3. Reset TCP/IP settings. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator and type the following commands, pressing Enter after each one:
– ipconfig /release
– ipconfig /renew
– netsh winsock reset
4. Disable antivirus software temporarily. Sometimes, antivirus software can interfere with network connections. Temporarily disable your antivirus program and check if the error persists.
5. Reset network settings. In Windows 10, you can reset your network settings to their default configurations. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network reset. Click on “Reset now” to initiate the reset.
Common Causes of IP Configuration Issues
- Incorrect network settings: Misconfigured network settings can lead to IP configuration issues.
- IP address conflicts: When two devices on the same network have the same IP address, conflicts occur.
- Faulty or outdated drivers: Outdated or malfunctioning network drivers can cause IP configuration problems.
- Firewall or antivirus interference: Overly restrictive firewall settings or antivirus software can block network communication.
- Router issues: Problems with the router’s firmware, settings, or hardware can result in IP configuration issues.
- Network cable or Wi-Fi connection problems: Faulty cables or weak Wi-Fi signals can prevent proper IP configuration.
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) failures: Issues with the DHCP server can prevent devices from obtaining valid IP configurations.
- Operating system glitches or bugs: Software issues within the operating system can cause IP configuration problems.
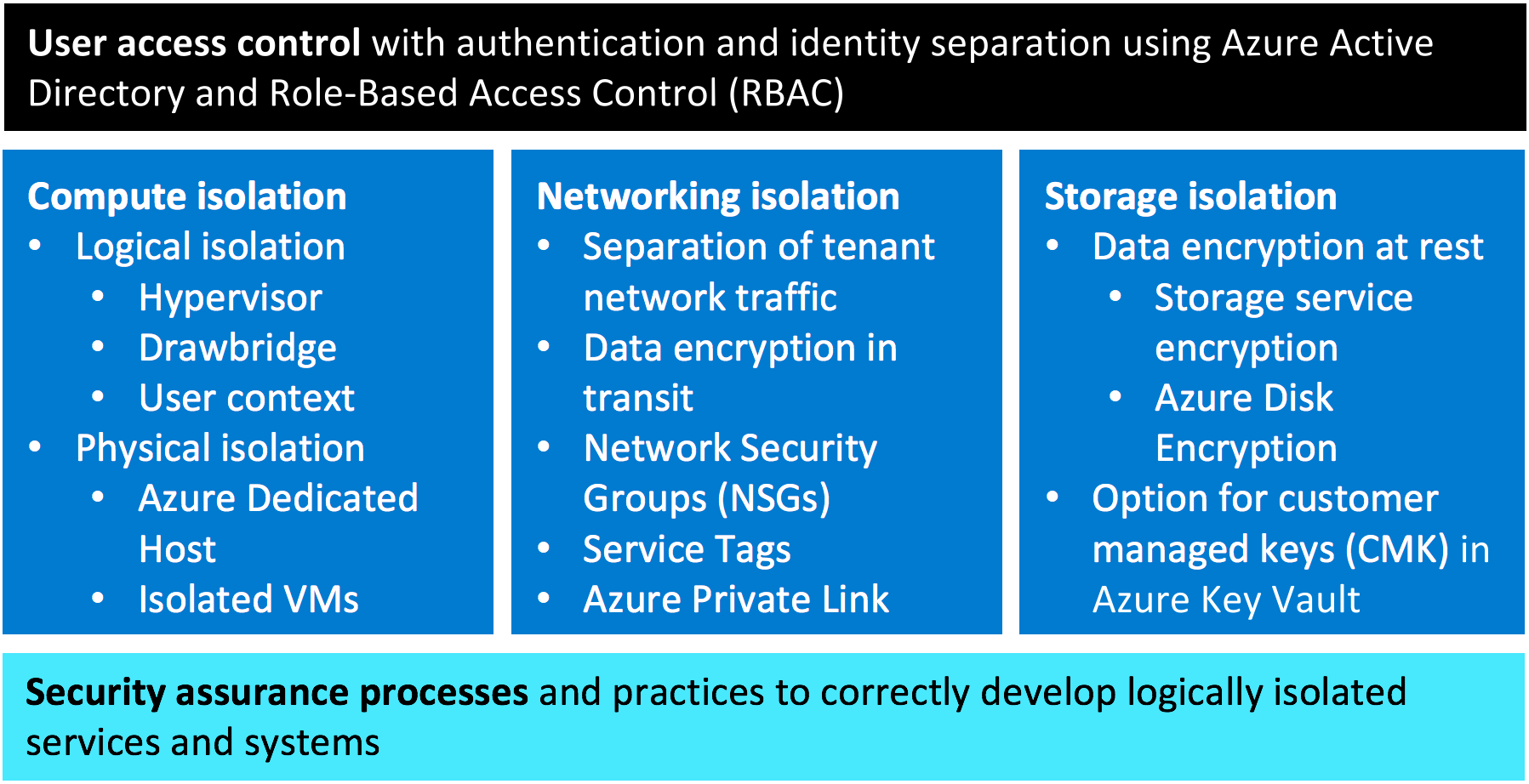
- Internet Service Provider (ISP) issues: Problems with the ISP’s network infrastructure or DNS servers can affect IP configuration.
Restart Your Network Devices
1. First, locate your router and modem. These are usually separate devices, but sometimes they are combined into one.
2. Disconnect the power cable from both the router and modem. This will turn them off completely.
3. Wait for about 30 seconds to a minute. This will allow any residual power to dissipate.
4. Reconnect the power cable to the modem first, and then to the router. Make sure they are securely plugged in.
5. Wait for the devices to power back on. This may take a few minutes. You can check the lights on the devices to see if they are fully powered on.
6. Once the lights indicate that the devices are back on, try connecting to your Wi-Fi or Ethernet again.
7. If you are still experiencing issues, you may need to troubleshoot further. You can try resetting your network settings, updating your drivers, or checking for any software conflicts.
Clean Boot Your Computer
1. Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “msconfig” (without the quotation marks) and press Enter.
3. In the System Configuration window, go to the Services tab.
4. Check the box next to “Hide all Microsoft services” to prevent disabling essential system processes.
5. Click on the “Disable all” button to disable all non-Microsoft services.
6. Next, go to the Startup tab and click on “Open Task Manager.”
7. In the Task Manager window, disable any startup items that are not necessary for your computer’s operation.
8. Close the Task Manager and go back to the System Configuration window.
9. Click on the “OK” button and restart your computer.
By clean booting your computer, you can eliminate any conflicting third-party software that may be causing issues with your Wi-Fi and Ethernet valid IP configuration. This can help resolve connectivity problems and improve your network performance.
Run Network Troubleshooter
To run the Network Troubleshooter on Windows 10 and fix Wi-Fi and Ethernet Valid IP Configuration issues, follow these steps:
1. Right-click on the Start menu and select “Settings” from the menu.
2. In the Settings window, click on “Network & Internet.”
3. In the Network & Internet settings, select “Status” from the left-hand menu.
4. Scroll down and click on the “Network Troubleshooter” option under the “Change your network settings” section.
5. The Network Troubleshooter will start detecting and fixing any network issues. Wait for it to complete the process.
6. Once the Network Troubleshooter finishes, it will provide a summary of the problems found and fixed (if any).
7. Follow any additional instructions provided by the Troubleshooter to resolve the Wi-Fi and Ethernet Valid IP Configuration issues.
Remember to restart your computer after running the Troubleshooter to apply any changes made.
If the Troubleshooter doesn’t resolve the issue, you may need to try other troubleshooting steps or seek further assistance from your Internet Service Provider or a professional technician.
Reset Network Adapter and TCP/IP Settings
To reset the network adapter and TCP/IP settings, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “cmd” and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
3. In the Command Prompt, type “netsh winsock reset” and press Enter to reset the Winsock catalog.
4. Wait for the process to complete, then restart your computer.
Next, we’ll reset the TCP/IP settings:
1. Open the Command Prompt again as administrator.
2. Type “netsh int ip reset” and press Enter to reset the TCP/IP stack.
3. Restart your computer once the process is finished.
By resetting the network adapter and TCP/IP settings, you can fix issues related to Wi-Fi and Ethernet valid IP configuration. These steps can resolve problems such as limited or no internet connectivity, unidentified network, or IP configuration errors.
Temporarily Disable Antivirus Software
To temporarily disable your antivirus software, follow these steps:
1. Locate the antivirus software icon in your system tray or taskbar. It’s usually near the clock in the bottom right corner of your screen.
2. Right-click on the antivirus software icon to open a menu.
3. Look for an option that says “Disable” or “Turn Off.” This may be labeled differently depending on the antivirus software you’re using.
4. Click on the “Disable” or “Turn Off” option. A confirmation prompt may appear.
5. Confirm your choice to disable the antivirus software temporarily.
6. Once the antivirus software is disabled, you can proceed with troubleshooting your Wi-Fi or Ethernet valid IP configuration issue.
Set IP Address Manually or Auto
- Open Network and Sharing Center
- Click on the network icon in the system tray
- Select “Open Network and Sharing Center”
- Access Network Adapter Properties
- Click on “Change adapter settings”
- Right-click on the network adapter in use
- Select “Properties”
- Configure IPv4 Properties
- Double-click on “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”
- Set IP Address Manually
- Select the option “Use the following IP address”
- Enter the desired IP address in the “IP address” field
- Enter the subnet mask in the “Subnet mask” field
- Enter the default gateway in the “Default gateway” field
- Enter the preferred and alternate DNS servers in the respective fields
- Set IP Address Automatically
- Select the option “Obtain an IP address automatically”
- Select the option “Obtain DNS server address automatically”
- Apply the Changes
- Click on “OK” to save the changes
- Close the Network Adapter Properties window
- Restart the computer for the changes to take effect
Update or Reinstall Network Adapter Drivers
To update or reinstall your network adapter drivers, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “devmgmt.msc” and press Enter to open the Device Manager.
3. In the Device Manager window, expand the “Network adapters” category.
4. Right-click on your network adapter and select “Update driver” or “Uninstall device” if you want to reinstall the driver.
5. If you chose to update the driver, select “Search automatically for updated driver software.” Windows will search and install the latest driver for your network adapter.
6. If you chose to uninstall the driver, follow the on-screen prompts and restart your computer. Windows will automatically reinstall the driver.
Updating or reinstalling your network adapter drivers can help resolve issues with Wi-Fi and Ethernet valid IP configuration. It ensures that your computer can properly communicate with the network interface controller and establish a connection to the router or wireless network.
Remember to restart your computer after updating or reinstalling the driver to apply the changes.
By keeping your network adapter drivers up to date, you can improve your internet connection, prevent connection drops, and resolve issues related to IP configuration.
Note: If you’re experiencing persistent network issues, you may also want to consider checking your firewall settings, resetting your router, or contacting your internet service provider for further assistance.
Stay connected and enjoy a seamless internet experience!
Reset Firewall to Default Settings
![]()
To reset your firewall to its default settings, follow these steps:
1. Open the Start menu by clicking on the Windows icon in the bottom left corner of your screen.
2. Type “firewall” into the search bar and select “Windows Defender Firewall” from the search results. This will open the Windows Defender Firewall settings.
3. In the left-hand menu, click on “Restore defaults” to reset the firewall to its original settings.
4. A confirmation dialog will appear. Click on “Yes” to proceed with the reset.
5. Once the reset is complete, you can close the Windows Defender Firewall settings window.
By resetting your firewall to its default settings, you can resolve any configuration issues that may be causing problems with your Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections. This can help ensure that your network interface controller and router are able to communicate properly with your wireless network, allowing for a valid IP configuration.
Remember to also check your network settings, such as your IP address and gateway, to ensure they are correctly configured. This can be done through the network settings menu on your computer.
If you continue to experience issues with your Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections after resetting the firewall, it may be worth considering other troubleshooting steps, such as updating your device drivers or checking for any software conflicts.
Network Reset to Default Configuration
To reset your network to its default configuration, follow these steps:
1. Open the Start menu by clicking on the Windows logo in the bottom left corner of your screen.
2. Type “Network reset” into the search bar and select the “Network reset” option from the results.
3. A new window will open with a warning message. Read the message carefully and click on the “Reset now” button to proceed.
4. Windows will now reset your network settings to their default configuration. This may take a few minutes.
5. Once the reset is complete, your computer will restart automatically. After the restart, you will need to reconnect to your Wi-Fi network or Ethernet connection.
Remember to have your Wi-Fi password or Ethernet cable ready for the reconnection process.
By resetting your network, you are essentially wiping out any custom configurations you may have made, such as static IP addresses or DNS settings. This can help resolve issues with your Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection if they are caused by misconfigured network settings.
If you are still experiencing issues with your network connectivity after resetting, it may be worth checking your router settings or contacting your internet service provider for further assistance.
Considerations: Ethernet vs. Wi-Fi Connections
| Consideration | Ethernet Connection | Wi-Fi Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Generally faster and more reliable | Speed can vary based on signal strength and interference |
| Security | More secure as it is a physical connection | Potentially less secure due to the possibility of interception |
| Convenience | Requires physical connection to router | Allows for mobility within Wi-Fi range |
| Interference | Less susceptible to interference | Can be affected by other devices and electronic interference |
| Cost | May require additional hardware (Ethernet cable) | No additional hardware required |
FAQs
What causes invalid IP?
Invalid IP addresses can be caused by a range of factors, including conflicts with other devices on the network and issues with network configuration.
Why does it say my Wi-Fi has no IP address?
It says your Wi-Fi has no IP address because there may be a router issue or your device may be blocked from connecting to the network.
How do I fix my IP address configuration?
To fix your IP address configuration, go to Start, then select Settings > Network & Internet. For a Wi-Fi network, select Wi-Fi > Manage known networks. Under IP assignment, select Edit. Under Edit IP settings, select Automatic (DHCP) or Manual. Finally, select Save.
How do I fix not having a valid IP configuration?
To fix not having a valid IP configuration, you can try the following steps:
1. Restart your Modem, Router, and Computer.
2. Disable the Fast Startup feature.
3. Configure your network adapter settings.
4. Reset TCP/IP.
5. Clear the network cache.
6. Reinstall/Update your Network Adapter Driver.
