In this article, I will discuss various troubleshooting methods to fix DNS server errors.
Understanding DNS Server Issues
When encountering DNS server issues, the first step is to check your internet connection. Ensure that you are connected to the Wi-Fi or Ethernet properly.
If the connection is stable, try flushing the DNS cache. In Windows, open Command Prompt and type ‘ipconfig /flushdns’. For MacOS, use the command ‘sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder’.
Another troubleshooting method is changing your DNS server. In Windows, go to Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings. Right-click on your network connection, select Properties, and then choose Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4). Enter Google’s DNS servers: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4.
If the issue persists, try accessing the website in Safe Mode. This will help determine if the problem is caused by a third-party application or extension.
Browser Troubleshooting Tips
To troubleshoot DNS server errors in your browser, try the following tips:
1. Clear the browser cache: In your browser settings, clear the cache to remove any stored data that may be causing the DNS server error.
2. Reset the browser: Resetting your browser to its default settings can help resolve DNS server errors.
3. Check your network connection: Ensure that you are connected to a stable network and try restarting your modem or router.
4. Use Google’s DNS: Change your DNS server settings to Google’s public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) to see if that resolves the issue.
5. Restart your computer: Sometimes a simple reboot can fix DNS server errors on your browser.
Computer DNS Troubleshooting
When troubleshooting DNS server errors on your computer, the first step is to check your internet connection. Ensure that your Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection is stable and working properly.
If you are using a web browser like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Safari, try clearing your browser cache and cookies. This can help resolve any DNS-related issues that may be causing website loading problems.
If the issue persists, try flushing your DNS cache. To do this on Windows, open Command Prompt and type “ipconfig /flushdns”. On MacOS, open Terminal and type “sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder”.
If you are still experiencing DNS errors, try changing your DNS server settings. You can switch to Google’s public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or OpenDNS (208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220) to see if that resolves the issue.
Another troubleshooting method is to restart your computer in safe mode. This can help identify if a third-party application or software is causing the DNS errors.
Router Troubleshooting Strategies

When troubleshooting DNS server errors on your router, try the following strategies:
First, check the physical connections to ensure everything is properly plugged in.
Next, restart your router by unplugging it for a few seconds and then plugging it back in.
If the issue persists, clear the DNS cache on your computer.
To do this on Windows, open the Command Prompt and type “ipconfig /flushdns”.
On a Mac, use the Terminal and type “sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder”.
If you are still experiencing issues, try changing your DNS server settings to Google’s public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or a different provider like OpenDNS.
Finally, update your router’s firmware to ensure it is running the latest version.
ISP-Related DNS Solutions
If you are still having issues, you can contact your ISP’s technical support for assistance. They may be able to provide further troubleshooting steps or identify any larger issues affecting your connection.
Switching Browsers for Better Connectivity
Switching browsers can sometimes improve connectivity issues related to DNS server errors. If you are experiencing problems with your current browser, try downloading a different browser such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Firefox, or Safari. Sometimes, the issue may be browser-specific and switching can help resolve it.
Additionally, consider clearing the cache and cookies on your browser to eliminate any stored data that may be causing the DNS server error. You can do this by accessing the settings or preferences menu in your browser and finding the option to clear browsing data.
If the problem persists, you may also want to check your network settings and ensure that your DNS server is set up correctly. You can do this by going to your computer’s Control Panel or System Preferences and looking for network settings or connections.
By switching browsers and checking your network settings, you can troubleshoot DNS server errors and improve your connectivity for a smoother online experience.
Utilizing Different Devices for Connection
- Check if other devices can connect to the network:
- Try connecting a different device, such as a smartphone or tablet, to the same network to see if the issue is with the specific device or the network itself.
- If other devices can connect successfully, the problem may lie with the original device’s settings or hardware.
- Restart the original device:
- Turn off the device completely and then turn it back on to see if this resolves the connection issue.
- Restarting the device can often reset network settings and resolve any temporary issues.
- Update network drivers:
- Check for any available updates for the network adapter drivers on the device experiencing connection issues.
- Updating drivers can address compatibility issues and improve network performance.
Safe Mode Startup Procedures
To start your computer in Safe Mode, begin by restarting your Windows operating system. As the computer boots up, press the F8 key repeatedly until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears. From there, select “Safe Mode” using the arrow keys and hit Enter. Safe Mode starts Windows with only essential drivers and services running, which can help troubleshoot DNS server errors.
Once in Safe Mode, open your web browser and check if the DNS server errors persist. If the issue is resolved, it may indicate a problem with a third-party application or service causing the error. You can then try uninstalling recently installed applications or performing a system restore to a point before the issue started.
If the DNS server errors continue in Safe Mode, it may be a deeper issue with your network settings or Windows configuration. Consider contacting technical support for further assistance or try other troubleshooting methods outlined in this article. Safe Mode can help isolate the problem and make it easier to pinpoint the cause of DNS server errors.
Antivirus and Firewall Adjustments
If you’re using Windows 10, go to the Control Panel and navigate to the “Windows Defender Firewall” settings. Ensure that the DNS server is allowed through both the public and private networks. If you’re using a different operating system, find the equivalent settings to make the necessary adjustments.
For antivirus software, locate the program on your computer and access the settings. Look for any options related to blocking certain connections or servers. Add the DNS server to the list of allowed connections to prevent any further issues.
After making these adjustments, try accessing the internet again to see if the DNS server errors have been resolved. If not, consider seeking further assistance or consulting online tutorials for additional troubleshooting methods.
Network Adapter Driver Updates
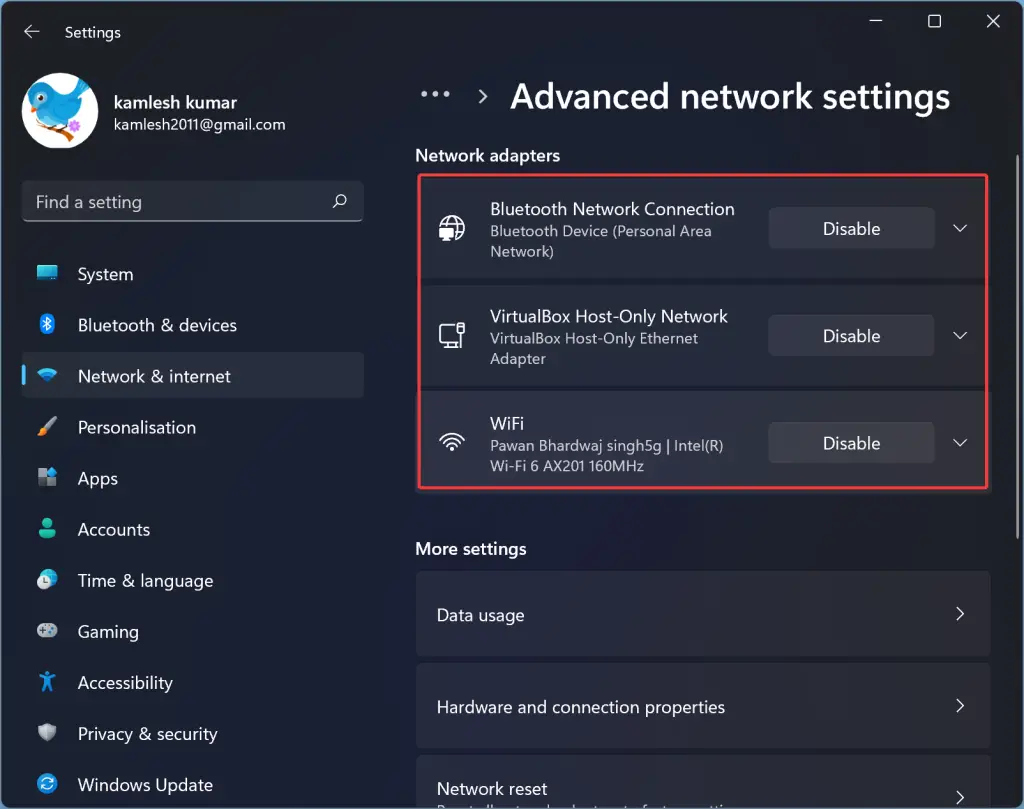
1. Right-click on the Start menu and select “Device Manager.”
2. Locate your network adapter under “Network adapters” and right-click on it.
3. Select “Update driver” and choose the option to automatically search for updated driver software.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the driver update process.
Updating your network adapter drivers can help resolve DNS server errors and improve your internet connection. Make sure to regularly check for driver updates to prevent similar issues in the future.
DNS Cache Maintenance
DNS Cache Maintenance: Clearing the DNS cache can help resolve server errors. To do this on Windows 10, open the Command Prompt by typing “cmd” in the search bar. Then, type “ipconfig /flushdns” and press Enter. This will clear the DNS cache on your computer.
If you are using a Mac, you can clear the DNS cache on Safari by going to the Safari menu, selecting “Clear History,” and checking “Cache. ” This will clear the DNS cache on Safari. Regularly clearing the DNS cache can help prevent server errors and improve internet connectivity.
DNS Server Alternatives and IPv6 Configuration

| DNS Server | Description |
|---|---|
| Google Public DNS | Google’s free DNS service that offers fast and reliable resolution of domain names. |
| OpenDNS | Another popular alternative DNS service that provides security features such as malware protection and content filtering. |
| Cloudflare DNS | A DNS service known for its privacy-focused features and fast resolution times. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How to fix DNS server error?
To fix a DNS server error, you can clear the cache, reboot your computer, check your hardware and wires, run a wizard, run an antivirus scan, check DHCP settings, and seek help from experts if needed.
How do I get rid of DNS server error?
To get rid of a DNS server error, you can troubleshoot network problems, restart your modem or router, deactivate antivirus and firewall, flush the DNS cache, and consider changing the DNS server address.
How can I reset my DNS server?
To reset your DNS server, you can use the Command Prompt. Simply enter “CMD” into the Start Menu search box and select Command Prompt. In the Command Prompt window, type “ipconfig /flushdns” and press ENTER. Remember to restart your computer after completing this process.
What are the symptoms of DNS server problems?
The symptoms of DNS server problems include being unable to access web-connected services like your browser or email, despite having a working internet connection. This can result in webpages timing out, displaying error messages, or showing a specific “DNS error” message.
